To extract product data from Amazon reliably, you need to understand the foundations of how web data is accessed and manipulated. If you’re new to this space, it helps to start with the basics of how websites are structured and how data is scraped, concepts that are core to modern scraping techniques.
Amazon actively detects and blocks scraping attempts, returning errors or misleading content. That’s where proxies and error handling in Python become essential tools in your toolkit.
In this guide, we’ll walk through how to scrape any Amazon product page using Python and proxies, with tips to avoid detection and keep your scraper running reliably.
We will extract the following data from the pages:
- Product Title
- Price
- Rating
- Availability
You will also learn how to rotate proxies, avoid captchas, and scale your scraper without getting blocked.
Why Scraping Amazon Is Difficult
Amazon employs multiple layers of anti-scraping defenses, including:
- IP rate limiting and blacklisting.
- JavaScript rendering for certain content.
- Captchas and temporary blocks.
- Geo-based content restrictions.
- User-Agent and header fingerprinting.
Using requests.get(url) without the right setup often leads to incomplete data or even a ban.
Setting Up Your Environment
Before we scrape anything, make sure Python and the required libraries are installed.
Install Python
If Python isn’t already installed:
- Download Python 3.x from python.org/downloads
- During installation, check “Add Python to PATH”.
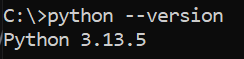
- Verify by running:
python --versionYou should see something like:
Install Required Libraries
Open your terminal or command prompt and install dependencies:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4These allow us to:
- Fetch HTML content from Amazon.
- Parse the HTML and extract relevant product data.
Use a Virtual Environment
For cleaner project management:
python -m venv amazon-scraper-env
source amazon-scraper-env/bin/activate # On Windows: amazon-scraper-env\Scripts\activate
pip install requests beautifulsoup4What Are We Scraping?
We will be scraping an Amazon product page for the demo:
Remember: This method applies to any Amazon product link.
Send Request with Proxy and Headers
Amazon blocks requests that don’t look like real browsers. Sometimes, sending only the User-Agent is enough to get the data, but at other times, you may need to send more headers.
To identify the User-agent by your browser, press F12 and open the Network tab. Select the first request and examine Request headers.
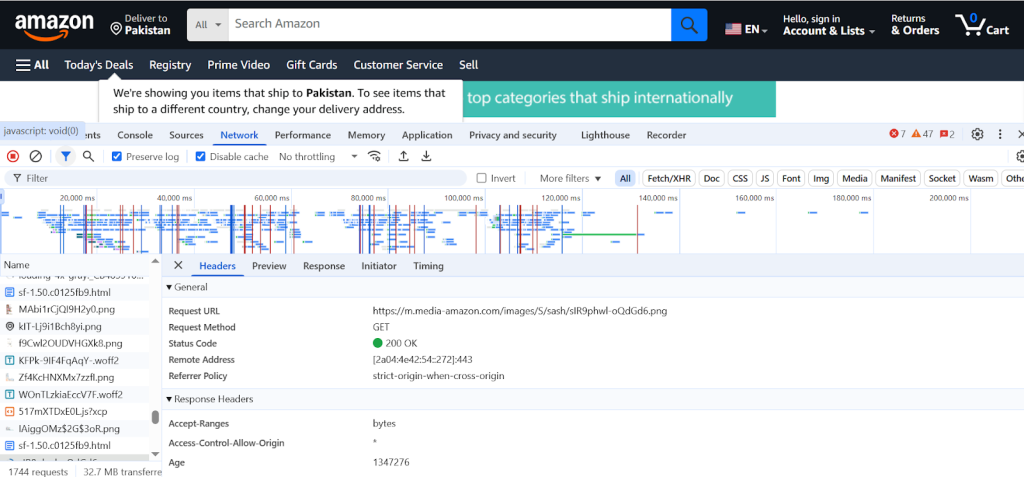
So we’ll add headers and use a proxy to make our requests look more like a regular browser.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = "https://www.amazon.com/dp/B098FKXT8L"
headers = {
"User-Agent": (
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) "
"AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) "
"Chrome/114.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
),
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9",
}
proxies = {
"http": "http://username:password@proxy.proxying.io:port",
"https": "http://username:password@proxy.proxying.io:port",
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")Replace the proxy URL, username, password, and port with your Proxying credentials.
Extract Product Information
Now that we have the page HTML, let’s pull the product data.
def extract_data(soup):
title = soup.find("span", id="productTitle")
price = soup.find("span", class_="a-offscreen")
rating = soup.find("span", class_="a-icon-alt")
availability = soup.find("div", id="availability")
return {
"Title": title.get_text(strip=True) if title else "N/A",
"Price": price.get_text(strip=True) if price else "N/A",
"Rating": rating.get_text(strip=True) if rating else "N/A",
"Availability": availability.get_text(strip=True) if availability else "N/A",
}
data = extract_data(soup)
print(data)Avoid Bot Detection with Proxies
Amazon may serve a captcha or an error page if you scrape too often from the same IP.
Fixes:
- Rotate IPs with each request
- Add delays
- Change headers
- Use residential proxies for better stealth
Proxying makes this easy with:
- Rotating endpoints
- Sticky sessions
- Datacenter and residential IPs
- Global locations for geo-unlocking
Rotate Proxies for Large-Scale Scraping
If you plan to scrape multiple products, you’ll need IP rotation:
import random
proxy_list = [
"http://user:pass@proxy1.proxying.io:port",
"http://user:pass@proxy2.proxying.io:port",
]
def get_random_proxy():
return random.choice(proxy_list)
response = requests.get(
url,
headers=headers,
proxies={"http": get_random_proxy(), "https": get_random_proxy()}
)Alternatively, use Proxying’s automatic rotating endpoint to handle this behind the scenes.
Save Scraped Data to CSV
Exporting your results makes them easier to work with later.
import csv
with open("amazon_product.csv", mode="w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as f:
writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=data.keys())
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerow(data)Add Retry and Delay Logic
Always retry failed requests and slow your scraper slightly to avoid rate limits.
import time
def safe_request(url, headers, proxies, retries=3):
for _ in range(retries):
try:
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies, timeout=10)
if "captcha" not in response.text.lower():
return response
except:
time.sleep(3)
return NoneUse Selenium for Dynamic Elements
If certain data is loaded via JavaScript (e.g., product variations or reviews), use a browser automation tool.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
options = Options()
options.add_argument("--headless")
options.add_argument("--proxy-server=http://user:pass@proxy.proxying.io:port")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)
driver.get(url)
print(driver.page_source)
driver.quit()Scrape Amazon in a Smart Way!
Scraping Amazon data may seem difficult at first, but with the right tools, Python, BeautifulSoup, and reliable proxies, it becomes pretty simple. Proxying offers lightning-fast, anonymous proxies ideal for Amazon scraping, data collection, and automation workflows.
- Datacenter and residential proxy pools
- Global IPs, sticky sessions, and auto-rotation
Sign up now and start scraping Amazon the smart way